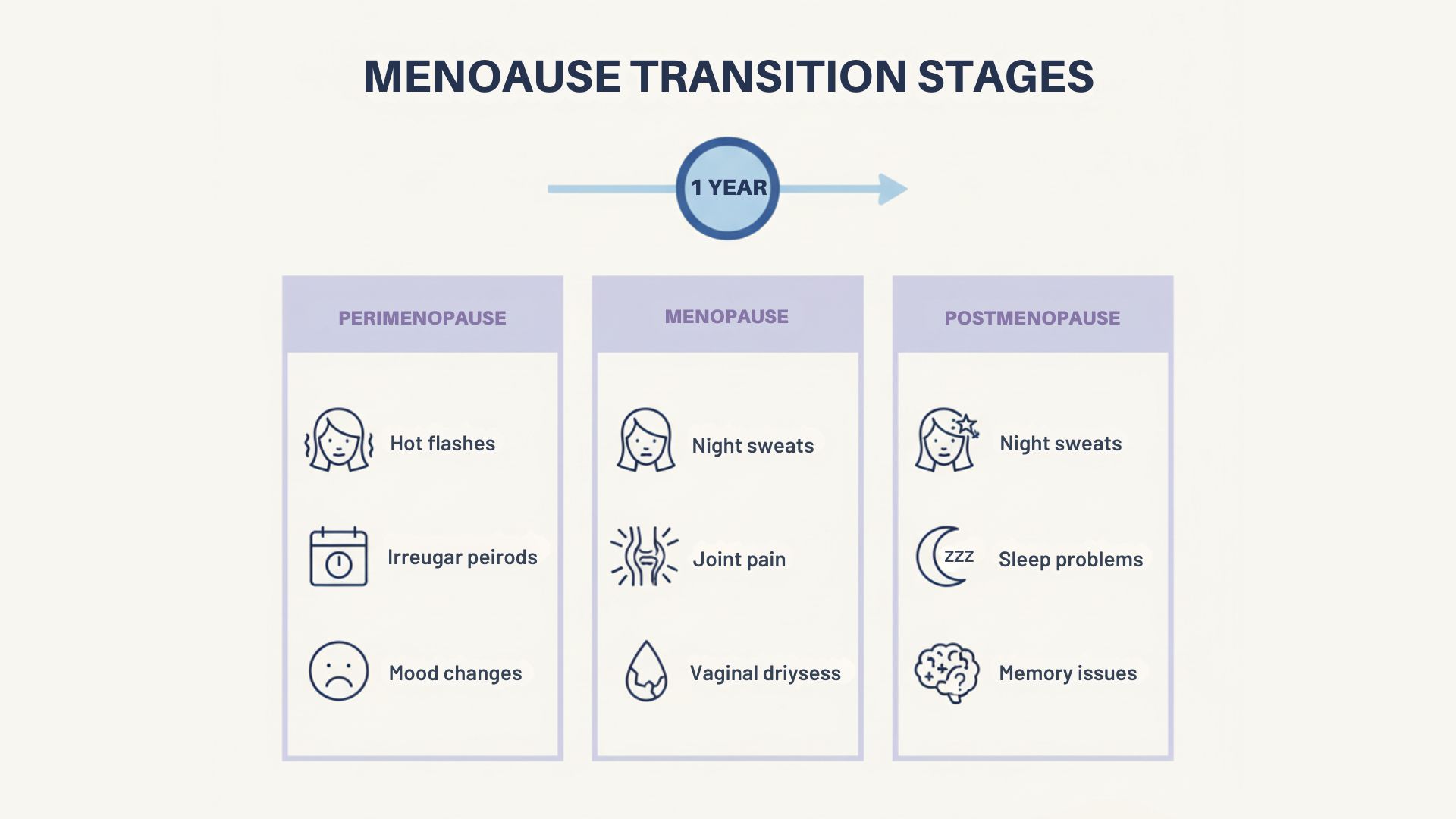
A Complete Guide to Hormone Replacement Therapy for Women and Menopause Relief
Hormone replacement therapy for women delivers effective symptom relief with substantially lower risks than earlier assumptions suggested. Current research demonstrates that hormone therapy remains safe when initiated before age 60 or within 10 years of menopause onset. The confusion surrounding hormone replacement therapy stems from decades of conflicting information and misinterpreted study data.
Evidence-based research reveals that HRT delivers benefits extending well beyond symptom management. The therapy provides essential protection against postmenopausal bone loss while significantly reducing fracture risk. Women experiencing vasomotor symptoms typically observe improvement within 1-2 weeks of treatment initiation. These rapid results make hormone therapy a viable solution for patients struggling with disruptive menopausal symptoms.
Treatment safety correlates directly with initiation timing. Women beginning therapy before age 60 or within the first decade following menopause experience benefits that substantially outweigh potential risks. A comprehensive 20-year follow-up investigation found no increased mortality from breast cancer or cardiovascular disease among hormone therapy participants. The same research revealed decreased all-cause mortality rates when treatment began before age 60.
Our clinical guidance addresses essential aspects of menopause hormone therapy selection. You’ll gain understanding of therapeutic mechanisms, available treatment modalities, and personalized assessment criteria for determining optimal candidacy.
What is HRT for women and how does it work?
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) functions as a targeted medical intervention designed to address menopausal symptoms through strategic hormone restoration. This therapeutic approach replenishes the declining hormones that naturally decrease during the menopausal transition.
Understanding hormone replacement therapy for menopause
HRT restores ovarian hormone levels that diminish naturally during menopause. The primary therapeutic objective centers on alleviating the spectrum of symptoms that impact quality of life during this physiological transition. Patients most commonly seek treatment for symptoms of menopause such as vasomotor symptoms, vaginal atrophy, mood disturbances, sleep disruption, and cognitive changes.
The FDA has approved HRT as the preferred first-line intervention for moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms. These manifestations include hot flashes, flushing, and hyperhidrosis occurring throughout day and night cycles. Symptom improvement typically becomes apparent within the initial weeks of treatment initiation.
Beyond symptomatic relief, HRT delivers substantial protective benefits. The therapy effectively prevents postmenopausal bone density loss while significantly reducing fracture risk. Patients frequently report enhanced sleep architecture and improved energy levels during treatment.
How estrogen and progesterone are used in HRT
Standard hormone replacement protocols utilize estrogen and progesterone combinations to restore the hormonal balance previously maintained by functional ovaries. Estrogen addresses the majority of menopausal symptoms, while progesterone serves essential protective functions within the treatment regimen, particularly concerning risks like uterine cancer.
Multiple estrogen formulations are available for therapeutic use:
- Conjugated equine estrogen (mixed estrogen compounds)
- Synthetic conjugated estrogens
- Micronized 17β-estradiol (bioidentical to ovarian estradiol)
- Ethinyl estradiol (predominantly utilized in contraceptive formulations)
Patients with intact uteri require concurrent progesterone therapy with estrogen administration. This essential combination prevents abnormal growth of the uterine lining, eliminating the endometrial cancer risk associated with unopposed estrogen therapy. Progesterone effectively prevents endometrial hyperplasia through its antiproliferative effects.
HRT delivery occurs through two primary modalities: systemic and localized therapy. Systemic estrogen administration distributes hormones throughout the body via oral tablets, transdermal patches, topical gels, or vaginal rings. This approach optimally manages widespread symptoms such as vasomotor disturbances. Localized therapy, including vaginal estrogen preparations, targets specific tissue areas with minimal systemic absorption.
What makes bioidentical hormone therapy different?
Bioidentical hormones represent laboratory-synthesized compounds engineered to replicate the molecular structure of endogenous hormones. These preparations originate from plant-derived precursors that undergo pharmaceutical processing to achieve molecular identity with human hormones. Estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone constitute the most frequently prescribed bioidentical hormone options.
Specific bioidentical formulations have received FDA approval for clinical use. These include micronized progesterone and estradiol preparations that maintain an identical molecular architecture to naturally occurring hormones. Alternative bioidentical preparations are compounded by specialized pharmacies according to individual prescriptions, termed compounded bioidentical hormones.
Public perception often positions bioidentical hormones as inherently safer and more natural alternatives to conventional hormone therapy. Current scientific literature provides limited evidence substantiating these safety claims. The North American Menopause Society has issued advisories regarding potential risks associated with bioidentical hormone use, emphasizing the importance of understanding the risks and benefits.
FDA-approved bioidentical formulations undergo extensive safety and efficacy evaluation protocols. Compounded preparations lack equivalent regulatory oversight and standardized testing. This regulatory gap potentially compromises dose accuracy and preparation purity in custom-formulated products.
Optimal HRT selection requires individualized assessment considering symptom profile, medical history, and patient preferences. Successful hormone therapy implementation typically necessitates specialized guidance from healthcare providers with dedicated menopause management expertise.
What are the main types of hormone therapy available?
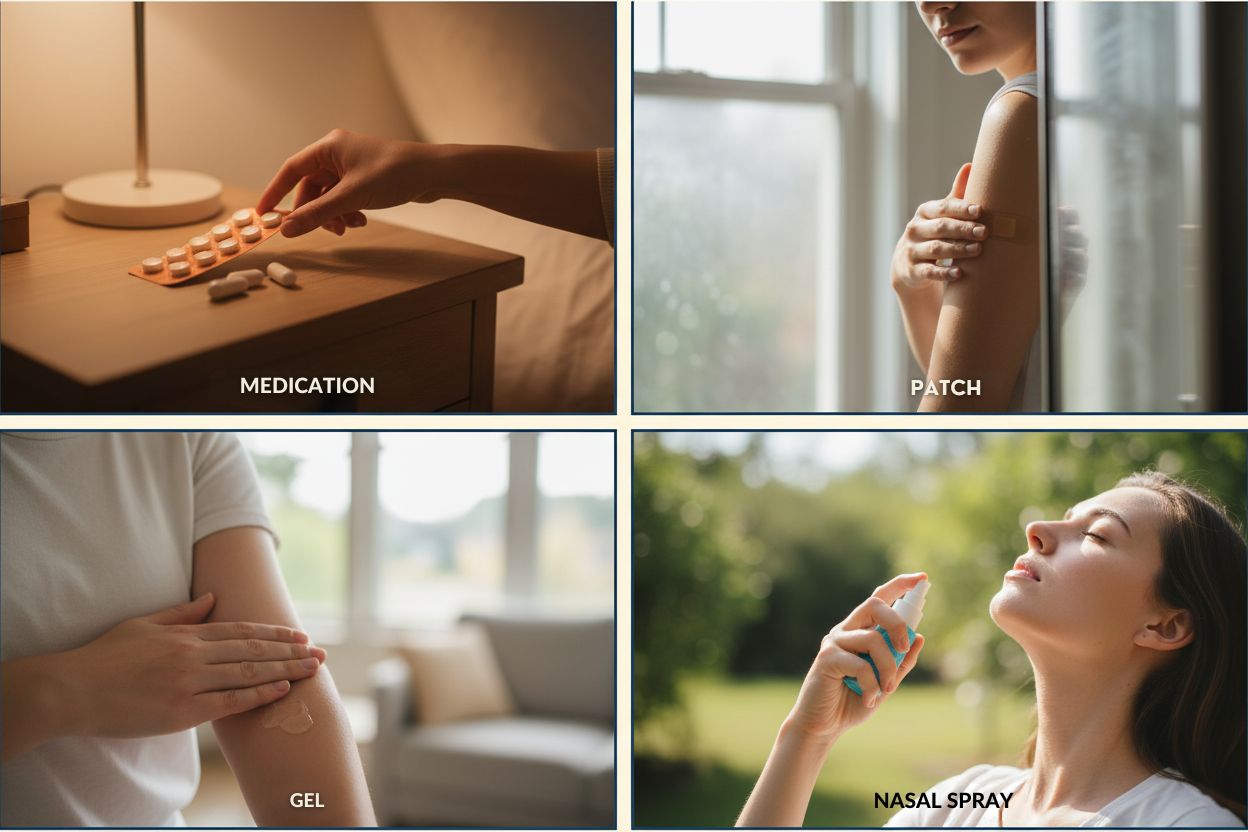

Treatment selection requires careful evaluation of individual symptom profiles and medical considerations. Clinical expertise guides the decision-making process to identify optimal therapeutic approaches for each patient’s unique circumstances.
Systemic vs local hormone therapy
Systemic hormone therapy provides whole-body hormone distribution through circulation, effectively addressing vasomotor symptoms, bone preservation, and systemic menopausal effects. Administration occurs through oral tablets, transdermal patches, topical gels, or nasal sprays.
Local hormone therapy delivers targeted treatment to specific tissues without substantial systemic absorption. This approach focuses primarily on genitourinary symptoms through vaginal creams, suppositories, or intravaginal rings. Minimal systemic absorption significantly reduces risk profiles compared to systemic alternatives.
Patients frequently report improvement in vaginal atrophy symptoms—including dryness, irritation, and dyspareunia—within several weeks of local therapy initiation. Clinical scenarios often warrant combined systemic and local approaches for patients experiencing both generalized and localized symptoms.
Estrogen-only vs combination therapy
Uterine status determines the fundamental therapeutic approach for hormone replacement.
Estrogen monotherapy suits patients following hysterectomy procedures. The absence of uterine tissue eliminates endometrial proliferation concerns associated with unopposed estrogen exposure.
Combination protocols incorporate estrogen with progestogen compounds to provide endometrial protection. This approach prevents abnormal uterine lining proliferation and associated malignancy risks. Patients with intact uteri require progestogen supplementation during systemic estrogen therapy.
Clinical protocols offer two primary combination patterns:
- Sequential regimens: Daily estrogen with cyclical progestogen administration (10-14 days monthly), typically producing withdrawal bleeding
- Continuous combined therapy: Daily administration of both hormones, generally eliminating regular bleeding episodes
Delivery methods: pellets, pills, patches, gels, and rings
Treatment modalities offer distinct clinical advantages based on patient needs and risk profiles.
Oral formulations provide convenient daily dosing. Hepatic first-pass metabolism slightly elevates thrombotic risk in susceptible patients. However, oral estrogen uniquely benefits lipid profiles through favorable cholesterol modifications.
Transdermal patches circumvent hepatic metabolism, reducing venous thromboembolism risk compared to oral preparations. Applied to lower torso areas, patches deliver consistent hormone levels with twice-weekly or weekly replacement schedules.
Topical gels and sprays represent additional non-oral options with rapid skin absorption. Complete drying prevents inadvertent transfer to family members or pets.
Vaginal preparations, including creams, tablets, and rings, provide direct tissue delivery. Ring devices remain effective for three-month periods, offering superior convenience over frequent applications.
Subcutaneous pellet implantation involves minor surgical placement of hormone-containing pellets, typically in the hip region. Professional medical societies discourage this approach due to safety concerns and lack of FDA regulatory approval.
Current best practices emphasize:
- Transdermal delivery systems over oral preparations for patients with increased thrombotic risk
- Bioidentical hormone formulations match endogenous molecular structures
- Minimum effective dosing strategies for symptom management
Specialized menopause care involves individualized treatment planning based on symptom severity, medical history, and patient preferences. Ongoing monitoring ensures therapeutic optimization while maintaining safety parameters.
When should women consider starting hormone therapy?
Clinical decision-making for hormone replacement therapy initiation requires careful evaluation of multiple patient-specific factors. Age, symptom severity, and menopausal timeline collectively influence the risk-benefit assessment that guides treatment recommendations.
Ideal age range for starting HRT
Scientific evidence consistently supports early intervention strategies for optimal therapeutic outcomes. Medical experts advocate for hormone therapy initiation before age 60 or within 10 years of your final menstrual period. This approach maximizes clinical benefits while maintaining favorable safety profiles.
Natural menopause typically occurs between ages 45 and 55, establishing the primary treatment consideration window. Perimenopausal women may benefit from earlier intervention, often during their fourth decade, when symptom management becomes necessary.
Optimal timing provides distinct clinical advantages for patients who initiate treatment during this therapeutic window:
- Enhanced symptom resolution
- Reduced long-term health risks
- Superior bone density preservation
- Potential cardiovascular protection
Women experiencing premature menopause (before age 40) or early menopause (before age 45) represent priority candidates for hormone therapy. Clinical protocols typically recommend treatment continuation until approximately age 51, corresponding to average natural menopause timing.
Why timing matters: the 10-year window
The therapeutic “10-year window” establishes a fundamental safety principle in menopause medicine. Clinical studies repeatedly confirm that women initiating HRT within this timeframe experience substantially lower risk profiles compared to delayed treatment approaches.
This temporal advantage reflects physiological changes in hormone receptor sensitivity and vascular responsiveness following estrogen withdrawal. Patients beginning treatment beyond age 60 or more than ten years post-menopause face elevated risks for thrombotic events, cerebrovascular complications, and cardiac issues.
Contemporary research validates this timing strategy. A significant investigation revealed that perimenopausal women using estrogen within the 10-year pre-menopause period demonstrated no increased incidence of breast cancer, myocardial infarction, or cerebrovascular events compared to control groups.
Furthermore, randomized controlled trials indicate that women initiating HRT within this critical window experience decreased mortality rates and reduced fracture incidence. These findings prompted FDA guideline revisions supporting treatment initiation within this optimal timeframe.
Signs you need hormone replacement therapy
Hormone therapy candidacy assessment centers on symptom impact and quality of life considerations. Approximately 75% of women develop night sweats, representing one of the most frequent treatment indications.
Clinical indicators suggesting hormone therapy benefits include:
- Vasomotor symptoms disrupting sleep architecture
- Mood alterations, including emergent anxiety or depression
- Menstrual irregularities or heavy bleeding (typically in the fifth decade)
- Vaginal atrophy causing discomfort or dyspareunia
- Concerns regarding bone health or cognitive function decline
Sleep disruption from vasomotor symptoms requires particular clinical attention. Chronic sleep fragmentation impacts both immediate functioning and long-term health outcomes. Women experiencing regular nocturnal awakenings should discuss therapeutic options with their healthcare providers.
Modern clinical practice supports early intervention rather than symptom severity thresholds. NHS guidelines recommend HRT discussions once bothersome symptoms emerge. Proactive treatment approaches typically yield superior outcomes.
Recent longitudinal research challenges previous assumptions about symptom duration. The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN) documented a median symptom duration of 7.4 years, with some women experiencing symptoms exceeding 11 years. These findings contradict earlier beliefs that menopausal symptoms resolve within 1-3 years.
Proactive healthcare planning includes hormone therapy discussions during routine examinations, particularly for women approaching their fifth decade. Early treatment planning enables optimal symptom management before potential symptom escalation.
What are the benefits of HRT for menopause symptom relief?
Hormone replacement therapy produces significant therapeutic outcomes across multiple menopause-related symptoms. Clinical observations show symptom improvement occurring within weeks of treatment initiation.
Nearly 8 in 10 women experience vasomotor symptoms during menopause, with episodes persisting for an average of seven years. Individual hot flash episodes typically span 1-5 minutes. Frequency varies considerably among patients, ranging from several weekly occurrences to as many as 30 daily episodes.
Vasomotor episodes manifest as sudden flushing of the face, neck, and chest regions. Excessive perspiration may occur, sometimes resulting in clothing saturation. These symptoms correlate directly with declining estrogen levels characteristic of menopause.
Hormone therapy addresses vasomotor symptoms by restoring estrogen balance, effectively reducing both episode frequency and intensity. Patients consistently report marked improvement in hot flash severity with appropriate hormonal intervention.
Mood swings and brain fog
Cognitive dysfunction represents a frequently overlooked yet prevalent menopause symptom. This mental cloudiness often presents alongside mood disorders and sexual health concerns.
Clinical studies identify severe depression and sexual dysfunction as primary factors correlating with cognitive performance decline. Patients in late postmenopausal stages demonstrate the highest scores for both depression and sexual dysfunction.
Mood stabilization shows a particularly strong response to hormone therapy. A 2015 NICE systematic review documented multiple studies demonstrating positive mood correlations with HRT utilization. Survey data indicate 47% of menopausal women experience depression, while 37% report anxiety symptoms.
Controlled clinical trials reveal significantly improved mood assessments among women receiving active hormone treatment versus placebo groups. Additional research demonstrates reduced depression incidence rates in patients using transdermal estrogen combined with progesterone over 12-month treatment periods.
Vaginal dryness and urinary symptoms
Estrogen deficiency creates substantial changes in vaginal tissue architecture, compromising lubrication, elasticity, pH balance, and vascular flow. These alterations frequently result in vaginal dryness, dyspareunia, and urogenital symptoms.
Postmenopausal vaginal microbiome changes include elevated pH levels and diminished protective lactobacillus populations, which can exacerbate symptoms of menopause. These conditions promote pathogenic bacterial growth and increase urinary tract infection susceptibility.
Vaginal estrogen applications provide effective therapeutic management for these symptoms while reducing UTI occurrence. Treatment mechanisms include enhanced vaginal epithelial elasticity, increased natural lubrication, and restoration of premenopausal pH levels.
Bone health and osteoporosis prevention
Hormone therapy significantly reduces vertebral, hip, and additional osteoporotic fracture risks across patient populations, including those at lower baseline risk. Traditional bone-preserving estrogen doses included oral estradiol 2 mg or conjugated equine estrogens 0.625 mg, though current research validates bone mass conservation with lower dosing protocols.
Continuous treatment regimens were historically recommended for optimal bone protection. Recent studies suggest that limited treatment duration during early menopause may provide sustained fracture reduction benefits.
Despite 2003 European regulatory guidance against HRT as primary osteoporosis prevention, many specialists continue advocating for its effectiveness, safety profile, and cost-efficiency. Estrogen-based interventions maintain particular clinical value for premature ovarian insufficiency patients.
Improved sleep and energy levels
Sleep disturbances affect 40-60% of women during perimenopause and early postmenopause. Chronic sleep quality impairment extends beyond mood effects, potentially contributing to cardiovascular disease and additional health complications.
Research published in Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society demonstrated effective sleep improvement with low-dose hormone therapy. HRT patients showed double the sleep quality enhancement compared to placebo recipients.
Treatment benefits include vasomotor symptom reduction that eliminates sleep disruption. Progesterone provides additional sleep support through its central nervous system sedative properties, facilitating sleep initiation. Estrogen contributes to REM sleep cycle stabilization, promoting restorative sleep patterns.
Hormonal balance optimization helps regulate cortisol rhythms, reducing stress-induced cortisol elevations that interfere with sleep architecture. This balance establishes consistent circadian patterns with reduced nocturnal restlessness.
HRT Safety Protocols and Risk Management Strategies
Contemporary research has fundamentally shifted our understanding of hormone replacement therapy safety profiles. The FDA removed misleading warnings after determining that appropriately timed HRT initiation provides substantial benefits that outweigh potential risks.
Clinical Risk Assessment: Breast Cancer, Thromboembolism, and Cerebrovascular Events
HRT risk profiles depend on multiple clinical variables: patient age, medical history, hormone formulation selection, and treatment duration.
Breast cancer risk analysis reveals:
- Estrogen monotherapy in hysterectomized patients demonstrates no increased breast cancer incidence
- Combined estrogen-progestogen therapy produces minimal risk elevation, comparable to moderate alcohol consumption
- Absolute risk increase remains clinically insignificant at less than 1 in 1,000 patients
Thrombotic and cerebrovascular risk parameters show variability. Clinical studies documented combined HRT increased stroke incidence by 41% and myocardial infarction rates by 29%. These elevated risks primarily affect patients initiating therapy after age 60.
Administration route significantly influences coagulation risk. Oral estrogen undergoes hepatic first-pass metabolism, generating prothrombotic factors. This hepatic processing increases venous thromboembolism risk 2-5 fold compared to non-users.
Delivery Method Impact on Safety Profiles
Transdermal delivery systems circumvent hepatic metabolism, substantially reducing thrombotic risk and offering benefits and risks that must be considered in the context of heart disease. The Estrogen and Thromboembolism Risk investigation demonstrated no increased clotting risk with transdermal patches, while oral formulations showed 4.2-fold risk elevation.
Optimal safety protocols include:
- Transdermal estrogen delivery (patches, gels) rather than oral administration
- Localized vaginal estrogen for genitourinary symptoms with minimal systemic absorption
- Micronized progesterone instead of synthetic progestins when indicated
Vaginal estradiol rings provide effective systemic vasomotor symptom management without increasing thrombotic risk.
Dosage Optimization and Bioidentical Hormone Selection
Lower-dose HRT protocols maintain therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. Sub-standard dosing continues to provide bone protection benefits, but the risks and benefits should be evaluated in the context of menopausal hormone therapies.
Bioidentical hormone categories include:
- FDA-approved bioidentical formulations with established safety and efficacy data
- Compounded bioidentical preparations lacking regulatory approval or standardized testing
FDA-approved bioidentical hormones like micronized progesterone demonstrate superior safety profiles compared to synthetic progestins. Research indicates no increased breast cancer risk during the initial five-year treatment periods with estrogen plus micronized progesterone.
Compounded bioidentical hormone claims lack supporting large-scale research validation. These preparations also lack quality control standards and appropriate monitoring protocols.
Clinical Monitoring and Surveillance Protocols
Regular clinical surveillance enables prompt risk identification and management. Healthcare providers implement:
- Periodic laboratory assessments for hormone level monitoring
- Dosage modifications based on symptom response and laboratory findings
- Appropriate screening protocols, including mammographic surveillance
- Ongoing treatment necessity evaluation at each clinical encounter
HRT patients require close clinical supervision, utilizing minimum effective dosing for the shortest appropriate duration. Standard screening protocols, including blood pressure monitoring and mammographic surveillance, remain essential.
Treatment initiation before age 60 or within 10 years of menopause significantly reduces risk profiles. Under these clinical parameters, studies demonstrate HRT reduces all-cause mortality by 30% and fracture incidence by 50-60%.
Personalized safety assessment requires individualized evaluation of risk factors, family history, and symptom profiles before treatment recommendations. This specialized approach ensures optimal therapeutic benefits with minimized risk exposure.
Who should avoid hormone therapy or use alternatives?
Certain medical conditions require alternative approaches to menopause management. Expert evaluation determines candidacy for hormone therapy while identifying optimal treatment strategies for women with contraindications.
Medical conditions that may rule out HRT
Systemic hormone therapy contraindications include:
- Breast or endometrial cancer
- Blood clots or clotting disorders
- Stroke or heart attack
- Liver disease
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding
Women aged 60 or older typically require alternative treatment approaches when initiating menopause management. Breast cancer survivors require specialized consultation, particularly those with estrogen-receptor-positive disease, where systemic HRT increases recurrence risk. Women carrying BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations face elevated lifetime risks that necessitate careful therapeutic consideration.
Non-hormonal menopause treatment options
FDA-approved pharmaceutical interventions provide effective symptom management without hormonal components. Paroxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, holds specific approval for vasomotor symptom treatment. The low-dose 7.5 mg formulation demonstrates a 10-25% reduction in symptom frequency versus placebo.
Additional prescription alternatives include:
- Antidepressant medications, including venlafaxine, escitalopram, and citalopram
- Fezolinetant, a neurokinin 3 receptor antagonist approved in 2023
- Gabapentin demonstrates a 10-20% symptom frequency reduction at 300 mg three times daily
- Oxybutynin addresses both vasomotor and bladder symptoms
- Clonidine, originally developed for cardiovascular applications
Vaginal symptoms respond to non-hormonal interventions, including lubricants and moisturizers. Lubricants provide immediate friction reduction during intercourse, while moisturizers offer sustained relief through tissue adherence.
Natural approaches for symptom management
Dr. JoAnn Manson, Professor of Women’s Health at Harvard Medical School, recommends initial lifestyle modification trials lasting approximately three months.
Mind-body interventions demonstrate clinical efficacy:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy produces measurable hot flash reduction
- Clinical hypnosis alleviates vasomotor symptoms
- Mindfulness-based stress reduction decreases symptom severity
Physical activity addresses multiple menopausal concerns, from weight management to sleep disturbances. Regular exercise provides cardiovascular protection benefits. Weight reduction particularly benefits women experiencing greater hot flash discomfort.
Supplement research yields variable results. Soy products containing high daidzein levels (converting to equol) show modest hot flash effectiveness with wide individual variation. S-equol supplementation at 10 milligrams twice daily may provide symptom control with minimal adverse effects.
Herbal preparations, including black cohosh, dong quai, ginseng, and wild yam, lack consistent clinical evidence supporting their efficacy. Healthcare provider consultation remains essential before initiating any supplement regimen due to potential medication interactions or safety concerns with specific medical conditions.
How do I personalize my HRT plan with a specialist?
Effective menopause management requires a partnership with healthcare professionals who prioritize your individual wellness journey. Successful hormone therapy depends on careful consideration of your unique physiological profile, symptom presentation, and long-term health objectives.
Working with a female hormone specialist
Selecting a qualified menopause specialist requires careful evaluation of their expertise and training credentials. Medical education gaps persist, with 80% of OB-GYN residents reporting inadequate preparation for menopause discussions. Seek practitioners with advanced certifications, particularly those designated as Menopause Society Certified Menopause Practitioners (NCMP) through The Menopause Society.
Optimize your consultation preparation through:
- Detailed symptom documentation spanning several weeks
- Quality-of-life impact prioritization
- Specific treatment inquiry preparation
- Complete medical and family history compilation
Customized hormone therapy for women
Expert menopause care centers on individualized treatment protocols tailored to your specific health profile. Your specialist evaluates benefit-risk ratios based on a comprehensive medical assessment. Advanced personalization incorporates targeted hormone optimization following thorough evaluation and ongoing symptom monitoring.
Optimal treatment design addresses both hormonal imbalances and lifestyle determinants. This integrative methodology targets underlying physiological disruptions rather than simply supplementing hormone deficiencies.
Hormone testing and dosage adjustments
Routine hormone level testing provides limited clinical value during perimenopause due to natural hormonal fluctuations. FDA guidelines discourage hormone level-guided dosing for menopausal women.
Specific clinical scenarios warrant hormone assessment:
- Atypical symptom presentation evaluation
- Concurrent thyroid dysfunction management
- Early menopause confirmation
- Post-surgical menopause following hysterectomy or endometrial ablation
- Testosterone therapy monitoring
Your provider prioritizes symptom-based treatment adjustments over laboratory values. Clinical excellence requires maintaining the minimum effective dose for the shortest therapeutic duration.
Finding the best menopause treatment clinic near you
Specialized menopause care demands advanced clinical training and expertise. Evaluate potential clinics based on their commitment to:
- Comprehensive pre-treatment laboratory assessment
- Structured follow-up monitoring protocols
- Integrated hormonal and non-hormonal treatment options
- Evidence-based lifestyle modification guidance
- Patient-centered communication and active listening
Investigate clinic approaches to bioidentical hormone therapy. FDA-approved bioidentical formulations undergo rigorous safety and efficacy validation, unlike compounded alternatives. Premier clinics emphasize FDA-approved treatments while maintaining flexibility for specialized clinical circumstances.
What are the latest updates and expert opinions on HRT?
Significant developments have reshaped the hormone replacement therapy landscape. The FDA’s historic decision to remove misleading “black box” warnings from HRT products after more than two decades reflects extensive scientific review demonstrating that benefits outweigh risks for appropriately selected women. This regulatory shift acknowledges decades of evidence supporting judicious hormone therapy use.
What Dr. Stile recommends for safe HRT options
Dr. Stile advocates for bioidentical hormones that precisely match naturally occurring hormone structures. These plant-derived formulations provide physiologically appropriate alternatives to synthetic hormone preparations. Dr. Stile’s evidence-based recommendations prioritize:
- Transdermal delivery systems, including patches and gels that circumvent hepatic first-pass metabolism
- FDA-approved bioidentical hormone formulations with established safety profiles
- Treatment initiation within the optimal 10-year post-menopausal window
How DrStileRx.com supports personalized menopause care
DrStileRx employs individualized treatment protocols for hormone therapy management. Each patient’s care begins with a thorough assessment of hormonal status and symptomatic presentation. The practice provides:
- Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy customized to specific physiological requirements
- Systematic monitoring protocols to ensure therapeutic optimization
- Expert guidance throughout the entire treatment continuum
New research on the long-term effects of HRT
Contemporary studies validate the critical importance of treatment timing for optimal outcomes. Women initiating HRT within the first decade post-menopause demonstrate:
- 50-60% reduction in osteoporotic fracture incidence
- Up to 50% decrease in cardiovascular disease risk
- 35% lower Alzheimer’s disease occurrence
A recent large-scale analysis examining data from over 120 million patient records found that perimenopausal women using estrogen therapy showed no elevated rates of breast cancer, myocardial infarction, or stroke compared to non-users. These findings support early treatment initiation for risk minimization.
The Women’s Health Initiative results, which previously generated concern, utilized hormone formulations no longer standard in clinical practice. Current research consistently demonstrates favorable outcomes for women beginning treatment before age 60, validating modern therapeutic approaches.
Conclusion
Hormone replacement therapy represents a clinically proven solution for women navigating menopausal symptoms. Evidence demonstrates optimal therapeutic outcomes when treatment begins before age 60 or within the first decade following menopause onset. This timing framework ensures maximum therapeutic benefit while minimizing potential adverse effects.
Treatment delivery systems require careful consideration based on individual patient profiles. Transdermal applications effectively circumvent hepatic processing, thereby reducing thrombotic complications compared to oral formulations, which is crucial for patients concerned about heart disease. Localized therapies provide targeted symptom management with minimal systemic exposure, making them a favorable option within the types of HRT available.
Individual health assessments remain paramount in treatment decision-making. Patients with histories of malignancy, thromboembolic disorders, or cardiovascular events benefit from non-hormonal therapeutic alternatives. FDA-approved pharmacological options and evidence-based lifestyle modifications offer effective symptom management strategies.
Specialist consultation significantly impacts treatment success. Board-certified menopause practitioners develop individualized protocols based on clinical presentation rather than laboratory values alone. This symptom-focused approach ensures appropriate therapeutic targeting.
Recent regulatory developments support improved treatment accessibility. FDA reassessment has eliminated outdated safety warnings following extensive scientific review demonstrating favorable risk-benefit profiles for appropriately selected candidates.
Therapeutic selection should integrate symptom severity, medical history, and personal treatment goals. Proper clinical guidance transforms the menopausal transition from a challenging health concern into a manageable life phase. Collaborative patient-provider relationships ensure optimal treatment selection, dosing precision, and sustained therapeutic success.
Key Takeaways
Understanding the timing, safety, and personalization of hormone replacement therapy can transform your menopause experience from challenging to manageable.
• Start HRT within the “golden window” – Begin before age 60 or within 10 years of menopause for maximum benefits and minimal risks
• Choose safer delivery methods – Patches and gels bypass the liver, reducing blood clot risks by up to 75% compared to oral pills
• Personalize your approach with specialists – Work with menopause-certified practitioners who tailor treatment based on symptoms, not just lab numbers
• Consider alternatives when needed – FDA-approved non-hormonal options like paroxetine effectively reduce hot flashes for women who can’t use HRT
• Recent research supports safety – The FDA removed misleading warnings after studies showed HRT reduces fractures by 50-60% and may lower cardiovascular disease risk when started appropriately
The key to successful menopause management lies in finding the right treatment approach for your unique situation, whether that’s bioidentical hormones, non-hormonal medications, or lifestyle modifications.
Take the Next Step:
Please fill out the form on this page to request an in-person consultation, and one of our knowledgeable medical staff members at DrStileRx will reach out to you promptly. You can also call our office directly at (702) 940-9925.
DrStileRx serves Las Vegas, NV, & Surrounding Areas.
*Individual results may vary
FAQs
What is the safest form of hormone replacement therapy for menopause?
The safest HRT options are typically transdermal methods like patches and gels, which bypass the liver and reduce blood clot risks. FDA-approved bioidentical hormones that match the structure of natural hormones are also considered safer. The key is to start therapy within 10 years of menopause onset or before age 60 for maximum benefits and minimal risks.
How can I manage menopause symptoms without hormone therapy?
There are several non-hormonal options for managing menopause symptoms. FDA-approved medications like paroxetine can help with hot flashes. Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and maintaining a healthy weight can also be effective. Some women find relief through cognitive behavioral therapy, clinical hypnosis, or mindfulness practices.
What are the potential risks associated with hormone replacement therapy?
While HRT offers many benefits, it can slightly increase the risk of breast cancer, blood clots, and stroke in some women. However, these risks are generally low when HRT is started at the appropriate time and dosage. The actual risk depends on factors like age, health history, and the type of hormone therapy used. Regular check-ups and screenings are important for monitoring any potential issues.
How long does it typically take for HRT to relieve menopause symptoms?
Many women notice improvements in symptoms like hot flashes and night sweats within 1-2 weeks of starting HRT. However, the full effects may take up to three months to develop. Vaginal symptoms often improve within a few weeks of starting local estrogen therapy. Your doctor may adjust your treatment plan if you don’t experience significant relief after several months.
Can HRT help with mood swings and cognitive issues during menopause?
Yes, hormone replacement therapy can help alleviate mood swings and cognitive symptoms like brain fog that often occur during menopause. Studies have shown that women using HRT report improved mood and cognitive function compared to those not on therapy. Estrogen plays a role in brain function, and replacing it can help stabilize mood and improve mental clarity for many women.
What are the benefits and risks of HRT for women?
Hormone replacement therapy (called hormone replacement therapy or HRT) can treat symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and genitourinary syndrome of menopause; estrogen therapy may help bone density and reduce fracture risk. However, HRT may also be associated with risks of HRT, including an increased risk of breast cancer and risk of developing breast cancer in some users, and a possible increased risk of blood clots and stroke depending on formulation and patient factors. The benefits and risks of HRT should be weighed individually with a clinician, considering age, time since onset of menopause, and personal and family cancer history.
When should I take HRT — should I start HRT before age 60 or after the onset of menopause?
Current guidance suggests that starting HRT before age 60 or within 10 years of the onset of menopause may provide greater benefits and lower some risks, particularly for systemic therapy aimed at moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms. For older women or those far from menopause onset, the risk profile changes, and therapy may need more careful consideration; decisions should follow individualized risk assessment and review of the 2022 hormone therapy position statement, where relevant.
What types of HRT are available, and how do they differ?
Types of HRT include estrogen-only HRT, combined HRT (estrogen plus progestogen), and continuous combined HRT (both hormones taken together daily). Systemic therapy delivers hormones throughout the body (pills, patches, gels) and can treat moderate to severe symptoms, while local vaginal estrogens address genitourinary syndrome of menopause with lower systemic exposure. Choice depends on whether you still have your uterus (progestogen therapy is added to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer) and which symptoms you seek to treat.
How can combined HRT and continuous combined HRT help treat symptoms of menopause?
Combined HRT (sequential or continuous combined) is used when a woman still has her uterus to protect against the risk of endometrial cancer from unopposed estrogen. Continuous combined HRT provides both estrogen and progestogen daily and may stabilize bleeding patterns over time. These regimens can effectively treat common symptoms of menopause, including symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats, while mitigating the risk of uterine cancer associated with estrogen-only use in women with a uterus.
What effects of hormone therapy should I expect, and what are the common menopause symptoms it treats?
Hormone therapy replaces declining estrogen (and sometimes progesterone), and hormone therapy may reduce common symptoms of menopause such as hot flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbance, mood changes, and genitourinary syndrome of menopause (dryness, painful intercourse, urinary symptoms). Effects vary by individual and product; some people see rapid improvement in vasomotor symptoms, while urogenital benefits may take longer or require local estrogen therapy.
Who should take HRT: who is a candidate to use hormone therapy?
Women experiencing menopause with moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms or genitourinary syndrome of menopause may take HRT to improve quality of life. Use of hormone replacement therapy is appropriate for many but contraindicated in people with certain histories (active breast cancer, unexplained vaginal bleeding, recent thromboembolism). A clinician will assess risks and benefits, including risks of HRT, such as the risk of developing breast cancer and other conditions, before recommending therapy products or systemic therapy.
How do I find help finding a certified menopause specialist to discuss therapy, may, risks, and benefits?
Ask your primary care physician or gynecologist for referrals to clinicians with menopause training, search professional society directories, or use local hospital referral services. A certified menopause specialist can explain the use of hormone therapy options, review personal and family risk of breast and ovarian cancer, discuss progestogen therapy if you still have your uterus, and tailor a plan to treat symptoms of menopause while minimizing risks and monitoring safety.
Are there cancer risks, such as increased risk of breast cancer or risk of endometrial cancer, with HRT?
Estrogen-only HRT increases the risk of endometrial cancer in women who still have a uterus unless progestogen therapy is added; this is why combined HRT is used. Combined regimens and some systemic therapies have been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer after several years of use; the magnitude depends on duration, hormone type, and individual factors. Discuss the risk of developing breast cancer and breast and ovarian cancer family history with your provider to decide if the benefits of hormone therapy outweigh the risks for you.

